
How to control the pressure and reduction on the tibiofibular joint. The inferior tibiofibular screw was surgically removed. There are some defects in screw fixation or suture-button devices. Some scholars have also reported the efficacy of suture-button devices in the treatment of Maisonneuve fracture.
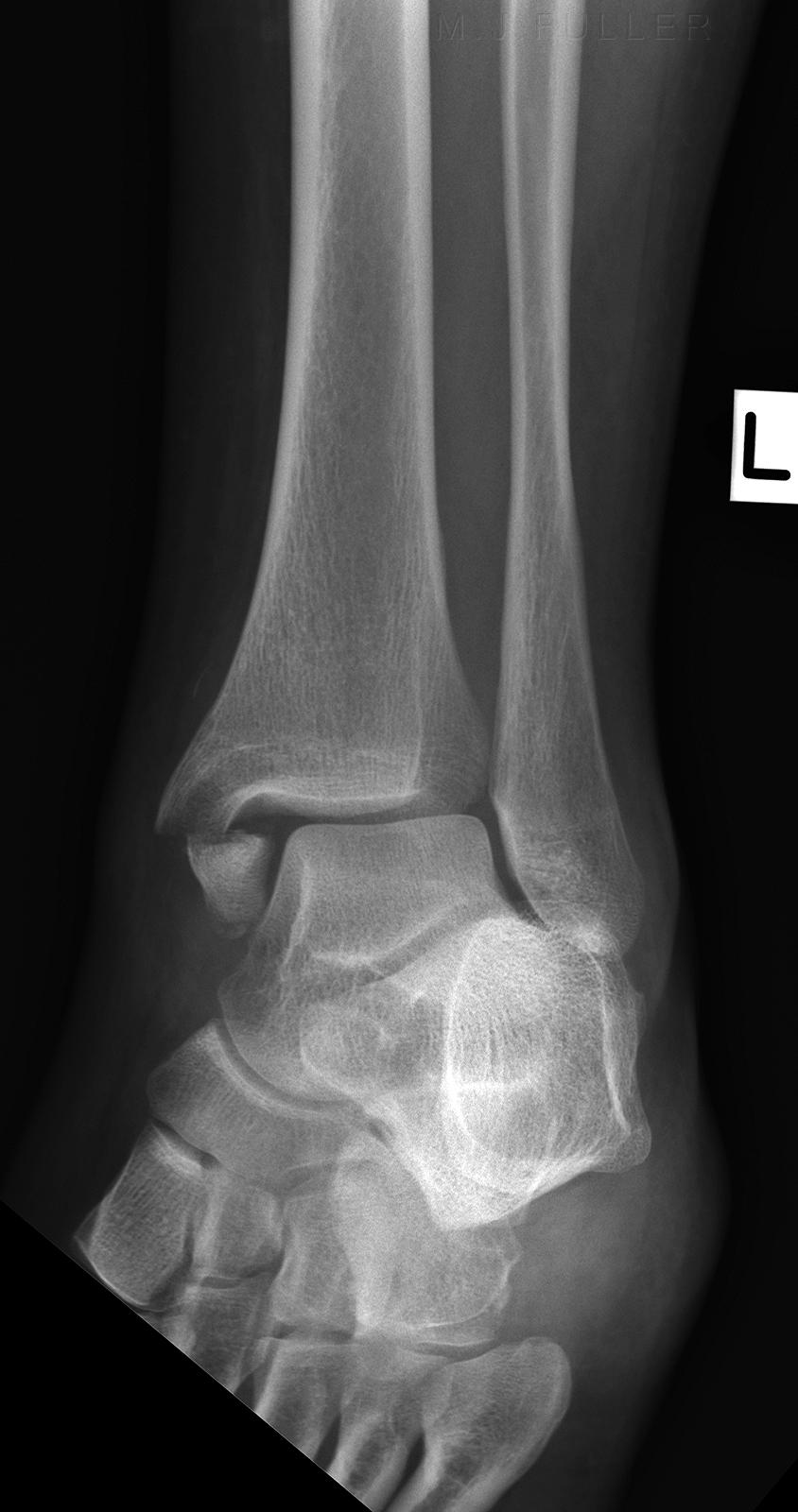
It is well known that the mainstream treatment option is the fixation of medial malleolus fracture, reduction of the inferior tibiofibular joint, and screw fixation. It is the rupture of the PITFL(posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament) or the avulsion fracture of the PITFL. If the rotational force doesn’t end, it’s the fourth stage. The second is the rupture of the AITFL(anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament) or avulsion fracture of the AITFL attachment point, the rupture of the IOL(interosseous ligament)and IOM(interosseous membrane), and the third is a fracture of the proximal fibula sometimes even without proximal fibula fractures. The first is medial malleolus fracture or deltoid ligament rupture, even the inside of the structure is complete. The damage mechanism of Maisonneuve fracture is the 3 or 4 stages of PER(pronation–external rotation) injury following Lauge–Hansen classification. įigure 8: X noted that the fracture healed without shortening or rotation of the fibula when twelve weeks after surgery.įracture of the fibula in approximately one-third is an important feature of Maisonneuve fracture. The AOFAS score is 92 at twelve weeks follow-up. X noted that the fracture healed without shortening or rotation of the fibula when twelve weeks after surgery (Figure 8). Ankle joint function exercises can be done three weeks after surgery.
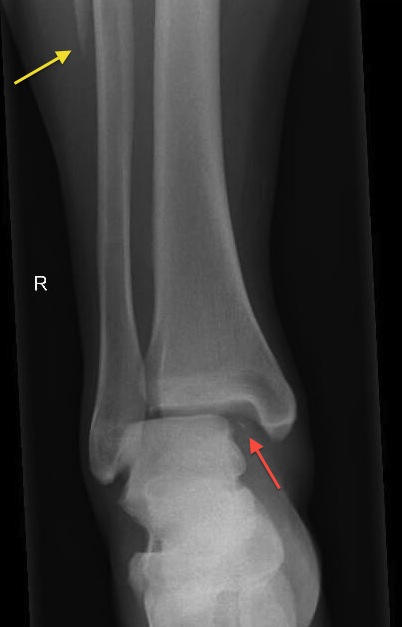
Patients are then allowed partial weight-bearing after six weeks and progress to weight-bearing. Three weeks after surgery, the patient is required to touch down weight-bearing in a plaster splint. The anterior and posterior ligaments of the inferior tibiofibular ligament are in good condition. It meant there was no dislocation of the distal fibula. CT scan in the transverse section confirmed that the anterior and posterior edge of the distal fibula is in an arc with the fractures of the tibia. Anatomical reduction and perfect stability were confirmed by X and CT postoperatively (Figures 6.7). Volkmann fracture was fixed by buttress plate, and Tillaux-Chaput fracture was performed by hollow screw. The inferior tibiofibular joint was checked carefully. An anterior tibial approach was used to expose the Tillaux-Chaput fracture. A posterolateral approach was used to expose the Volkmann fracture. The anesthetic for the operation was lumbar anesthesia. A computed tomography scan confirmed the presence of Tillaux-Chaput and Volkmann fractures (Figures 3-5). X-ray showed fractures in the tibia lateral border and fibular neck, with no evidence of inferior tibiofibular joint dislocation (Figures 1,2). Specialized physical examination found tenderness in the anterolateral distal tibia and fibular neck. She had difficulty walking because of a painful left ankle. She sprained her left ankle when she went down the stairs. Case descriptionĪ 56-year-old woman was sent to the emergency department by her family. The aim of this study is to introduce a new method-Maisonneuve without transsyndesmotic fixation and analysis the follow-up result. When the fibula fractured is without shortening or dislocation, it is still controversial if the inferior tibiofibular joint needs fixation. Operative treatment includes medial malleolus fixation, reduction of the inferior tibiofibular joint, and screw fixation. According to the Lauge - Hansen classification, it is a pronation and external rotation type injury, often resulting in inferior tibiofibular injury. Because it is extremely unstable, it is usually treated surgically. This fracture is usually caused by rotational force.
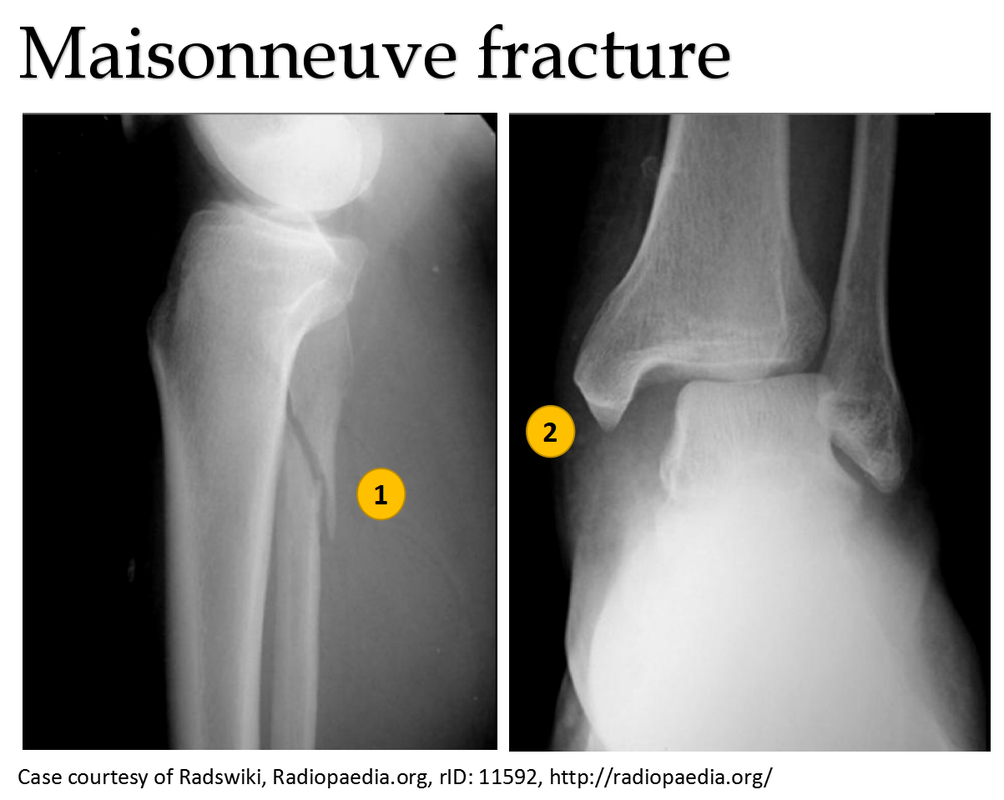
Associated with the posterior tibiofibular ligament or fractures of the posterior malleolus injures sometimes. It includes injury of the medial structure (medial malleolus fracture or deltoid ligament tear), inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis injury, and proximal 1/3 fracture of the fibula. The Maisonneuve fracture was first reported by the French doctor Maisonneuve in 1840. Ankle fracture is one of the common injuries in the orthopedic department.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
